
Clarence Hailey Long, 1949 - Another Landmark Image
This is C.H. Long, a 39-year-old foreman at the JA ranch in the Texas panhandle, a place described as “320,000 acres of nothing much.” Once a week, Long would ride into town for a store-bought shave and a milk shake. Maybe he’d take in a movie if a western was playing. He said things like, “If it weren’t for a good horse, a woman would be the sweetest thing in the world.” He rolled his own smokes. When the cowboy’s face and story appeared in LIFE in 1949, advertising exec Leo Burnett had an inspiration. The company Philip Morris, which had introduced Marlboro as a woman’s cigarette in 1924, was seeking a new image for the brand, and the Marlboro Man based on Long boosted Marlboro to the top of the worldwide cigarette market.
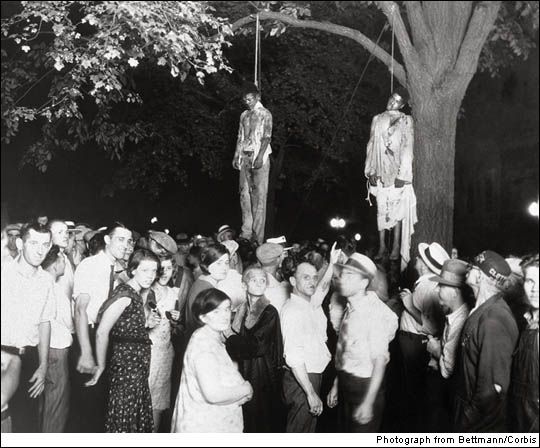

Lynching 1930
A mob of 10,000 whites took sledgehammers to the county jailhouse doors to get at these two young blacks accused of raping a white girl; the girl’s uncle saved the life of a third by proclaiming the man’s innocence. Although this was Marion, Ind., most of the nearly 5,000 lynchings documented between Reconstruction and the late 1960s were perpetrated in the South. (Hangings, beatings and mutilations were called the sentence of “Judge Lynch.”) Some lynching photos were made into postcards designed to boost white supremacy, but the tortured bodies and grotesquely happy crowds ended up revolting as many as they scared. Today the images remind us that we have not come as far from barbarity as we’d like to think.

Migrant Mother 1936
This California farmworker, age 32, had just sold her tent and the tires off her car to buy food for her seven kids. The family was living on scavenged vegetables and wild birds. Working for the federal government, Dorothea Lange took pictures like this one to document how the Depression colluded with the Dust Bowl to ravage lives. Along with the writing of her economist husband, Paul Taylor, Lange’s work helped convince the public and the government of the need to help field hands. Lange later said that this woman, whose name she did not ask, “seemed to know that my pictures might help her, and so she helped me.”
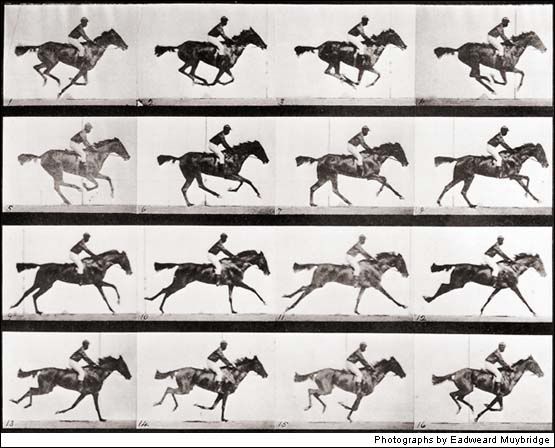
Galloping Horse 1878
Was there a moment midstride when horses had all hooves off the ground? Leland Stanford, the railroad baron and future university founder, bet there was—or at least that’s the story. It was 1872 when Stanford hired noted landscape photographer Eadweard Muybridge to figure it out. It took years, but Muybridge delivered: He rigged a racetrack with a dozen strings that triggered 12 cameras. Muybridge not only proved Stanford right but also set off the revolution in motion photography that would become movies. Biographer Rebecca Solnit summed up his life: “He is the man who split the second, as dramatic and far-reaching an action as the splitting of the atom.”
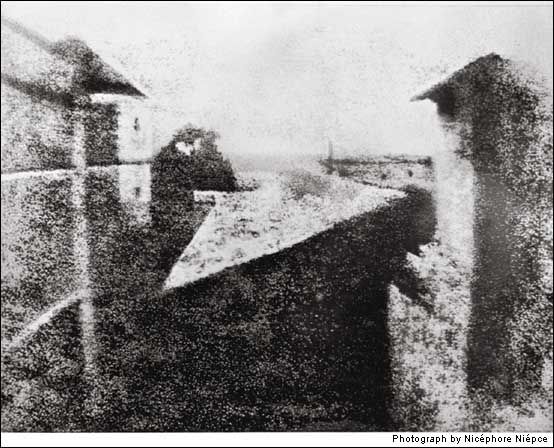

Pigeon House and Barn 1827
As early as 1793, Frenchman Nicéphore Niépce and his brother Claude imagined a photographic process, and over the next several years, Nicéphore experimented with various light-sensitive substances and cameras. In 1824 he produced a view from his window on a metal plate covered with asphalt. That and most other pictures fashioned by Niépce in the 1820s no longer exist, but the fuzzy image of a pigeon house and a barn roof taken in the summer of 1827 is a good representation of Niépce’s art. To make what he called a “heliograph,” or sun drawing, Niépce employed an exposure time of more than eight hours. Photography, if not yet practical, had been invented.
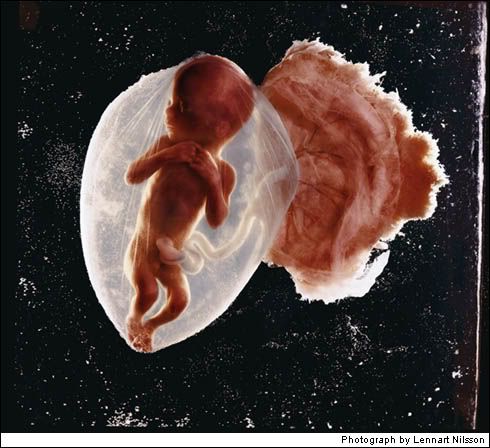
How Life Begins 1965
In 1957 he began taking pictures with an endoscope, an instrument that can see inside a body cavity, but when Lennart Nilsson presented the rewards of his work to LIFE’s editors several years later, they demanded that witnesses confirm that they were seeing what they thought they were seeing. Finally convinced, they published a cover story in 1965 that went on for 16 pages, and it created a sensation. Then, and over the intervening years, Nilsson’s painstakingly made pictures informed how humanity feels about . . . well, humanity. They also were appropriated for purposes that Nilsson never intended. Nearly as soon as the 1965 portfolio appeared in LIFE, images from it were enlarged by right-to-life activists and pasted to placards.
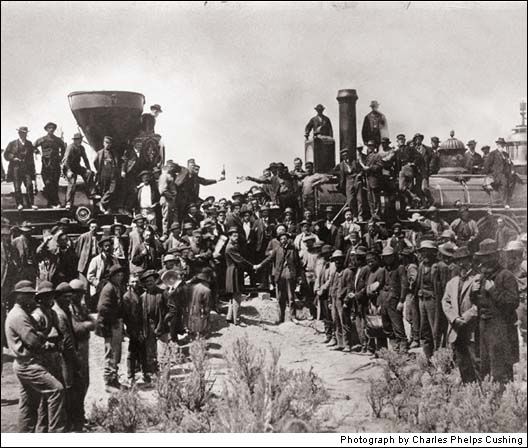

Promontory Point 1869
The ceremony begins on May 10, 1869, as an eastbound Central Pacific locomotive and a westbound Union Pacific locomotive meet in Promontory Point, Utah, marking the completion of the first transcontinental railroad. The men on the cowcatchers are ready to toast the driving of the golden spike. The work had been brutal. At one stage, efforts to tunnel through the marble spine of a Sierra Nevada mountain consumed an entire year, as only eight inches a day of progress was possible. So: a fabulous accomplishment. But this is also an early example of a photo op—the use of a picture as a means to an end. Folks back East could see, plain as day, that a train could take them all the way to California, where businessmen anxiously awaited their commerce

Triangle Shirtwaist Company Fire 1911
The Triangle Shirtwaist Company always kept its doors locked to ensure that the young immigrant women stayed stooped over their machines and didn’t steal anything. When a fire broke out on Saturday, March 25, 1911, on the eighth floor of the New York City factory, the locks sealed the workers’ fate. In just 30 minutes, 146 were killed. Witnesses thought the owners were tossing their best fabric out the windows to save it, then realized workers were jumping, sometimes after sharing a kiss (the scene can be viewed now as an eerie precursor to the World Trade Center events of September, 11, 2001, only a mile and a half south). The Triangle disaster spurred a national crusade for workplace safety.
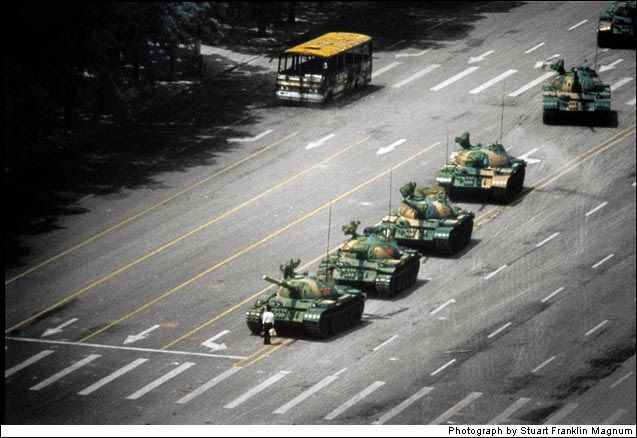

Tiananmen Square 1989
A hunger strike by 3,000 students in Beijing had grown to a protest of more than a million as the injustices of a nation cried for reform. For seven weeks the people and the People’s Republic, in the person of soldiers dispatched by a riven Communist Party, warily eyed each other as the world waited. When this young man simply would not move, standing with his meager bags before a line of tanks, a hero was born. A second hero emerged as the tank driver refused to crush the man, and instead drove his killing machine around him. Soon this dream would end, and blood would fill Tiananmen. But this picture had shown a billion Chinese that there is hope.
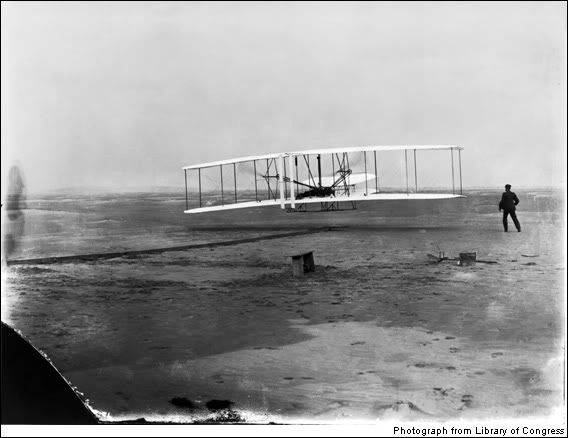

Flight 1903
On December 17, 1903, two bicycle mechanics from Ohio realized one of humanity’s wildest dreams: For 12 seconds they were possessed of true flight. Before the day ended, Orville and Wilbur Wright would keep their wood-wire-and-cloth Flyer aloft for 59 seconds. Sober citizens knew that only birds used wings to take to the air, so without being at the site, near Kitty Hawk, N.C., or seeing this photo, few would have believed the Wrights’ story. Although it had taken ages for humans to fly, once the brothers made their breakthrough, the learning curve reached the heavens. Within 15 years of this critical moment, nearly all the elements of the modern airplane had been imagined, if not yet developed.
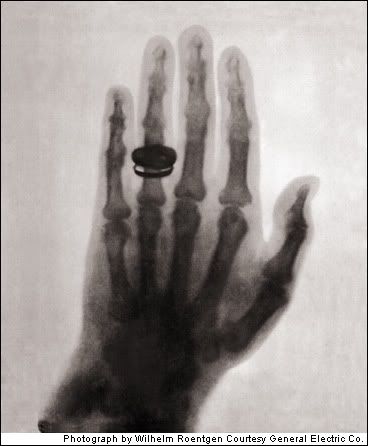
First Human X-ray 1896
To know something like the back of your hand is a timeless concept, one taken yet further by Wilhelm Konrad Roentgen. While working on a series of experiments with a Crookes tube, he noticed that a bit of barium platinocyanide emitted a fluorescent glow. He then laid a photographic plate behind his wife’s hand (note the wedding rings), and made the first X-ray photo. Before that, physicians were unable to look inside a person’s body without making an incision. Roentgen was the recipient of the first Nobel Prize for Physics in 1901.

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar